A dangerous low blood pressure for a woman is when it falls below 90/60 mmHg, causing symptoms like dizziness, fainting, and fatigue. Low blood pressure can restrict blood flow to vital organs, leading to serious health complications and should be monitored closely and treated promptly to avoid any harm.
Low blood pressure can be caused by various factors such as medications, dehydration, heart conditions, or hormonal fluctuations. It is crucial for women to consult a healthcare professional if experiencing persistent low blood pressure symptoms to evaluate the underlying cause and determine the appropriate treatment to maintain a healthy blood pressure level.
Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments can help manage and prevent dangerous low blood pressure in women.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/low-blood-pressure-signs-symptoms-and-complications-4689152-v1-55edb3baf5e944ce9c17fc6f29506bc1.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Understanding Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is too low. While high blood pressure is a common concern, low blood pressure can also pose health risks, especially for women. Understanding the definition, causes, symptoms, and risks of low blood pressure is important for maintaining optimal health.
Definition And Causes
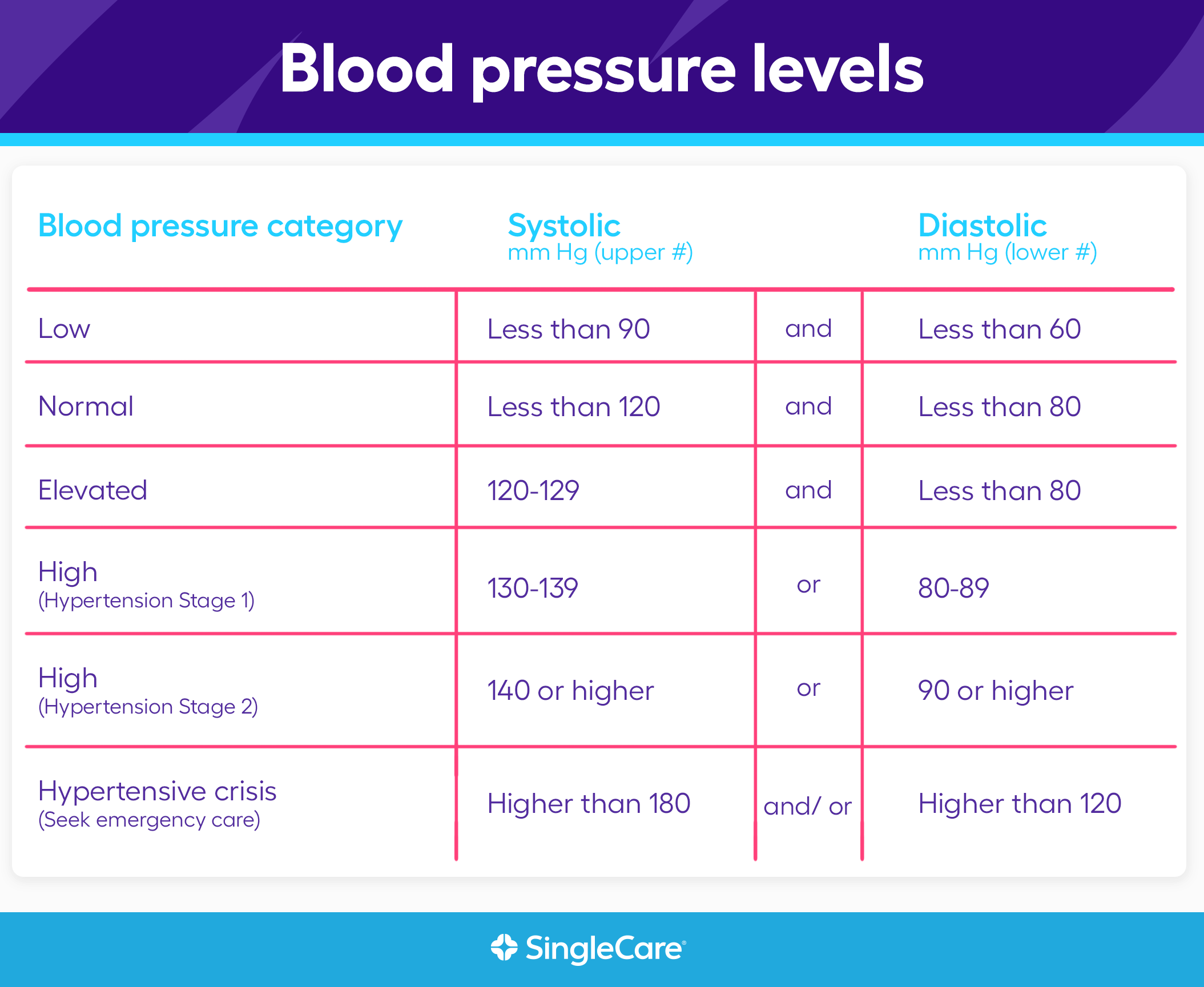
Low blood pressure is typically defined as a reading below 90/60 mmHg. The top number (systolic pressure) represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats, while the bottom number (diastolic pressure) represents the pressure between heartbeats. Low blood pressure can be caused by various factors, including:
- Dehydration
- Heart conditions such as bradycardia (slow heart rate) or heart valve problems
- Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy
- Blood loss due to injury or internal bleeding
- Medications that lower blood pressure
- Neurological disorders
Symptoms And Risks
While low blood pressure is generally considered favorable, extreme drops can trigger symptoms that may indicate underlying health issues. Some common symptoms related to dangerously low blood pressure levels include:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Blurry vision
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Rapid or shallow breathing
- Cold, clammy skin
For women, low blood pressure can pose additional risks, especially during pregnancy. Pregnant women with low blood pressure may experience complications, such as reduced blood flow to the uterus and fetus, leading to slower growth and development. Severe drops in blood pressure can also cause inadequate blood supply to vital organs like the brain, heart, and kidneys, potentially leading to organ damage.

Credit: www.healthproductsforyou.com
Normal Blood Pressure Ranges For Women
Healthy Blood Pressure Levels
For adult women, a healthy blood pressure reading is typically considered to be around 120/80 mm Hg. This is commonly known as the benchmark for normal blood pressure in the medical community.
Differences By Age And Health Conditions
Age can be a significant factor in blood pressure levels for women. As women age, their blood pressure may naturally rise. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help keep it within a normal range.
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, can also play a role in blood pressure. Women with pre-existing conditions should work closely with healthcare providers to monitor their blood pressure and make necessary adjustments to maintain a healthy range.
Signs Of Dangerous Low Blood Pressure
Dangerous low blood pressure for women can lead to dizziness, fainting, and fatigue. Sudden drops in blood pressure may cause blurred vision and confusion, posing serious health risks. Symptoms such as rapid breathing, shallow pulse, and cold, clammy skin should not be ignored and prompt medical attention is crucial.
Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, is generally considered normal if it doesn't cause any symptoms or complications. However, when blood pressure drops too low, it can become a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. In this section, we will explore the signs that indicate dangerously low blood pressure in women.
When To Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following signs of dangerously low blood pressure, it is crucial to seek medical attention right away:
1. Severe dizziness or lightheadedness: Feeling weak or faint, as if you might pass out, is an important indicator that your blood pressure is dangerously low. Any sudden, unexplained bouts of dizziness should not be ignored.
2. Rapid or shallow breathing: Difficulty in catching your breath or breathing rapidly can indicate that your organs are not receiving enough oxygen due to inadequate blood flow caused by low blood pressure.
3. Cool and moist skin: Clamminess or coolness in your skin, particularly on your extremities, could be a sign of dangerously low blood pressure. This occurs because blood vessels constrict to redirect blood flow to vital organs, compromising circulation to the skin.
4. Rapid or weak pulse: A rapid, irregular, or weak pulse can suggest that your heart is struggling to pump blood efficiently due to insufficient blood pressure. Pay attention to any unusual changes in your heart rate.
5. Confusion or disorientation: Low blood pressure can affect brain function, leading to confusion, difficulty concentrating, or feeling disoriented. If you notice these symptoms, seek medical help promptly.
Complications And Dangers
While low blood pressure may not always be immediately life-threatening, certain complications and dangers can arise if left untreated:
1. Organ damage: Insufficient blood flow can cause damage to vital organs such as the brain, heart, and kidneys. Prolonged low blood pressure can lead to heart attacks, strokes, or kidney failure.
2. Loss of consciousness: Deteriorating blood pressure levels can potentially cause loss of consciousness. Fainting or blacking out can result in injuries, especially if it occurs while performing tasks such as driving or operating machinery.
3. Shock: Extreme cases of low blood pressure can result in a life-threatening condition called hypovolemic shock. This occurs when blood volume drops significantly, impairing vital body functions and potentially leading to organ failure.
4. Reduced quality of life: Constant fatigue, weakness, and dizziness due to chronically low blood pressure can greatly impact a woman's quality of life, making it challenging to perform daily activities and enjoy regular physical exertion.
It is crucial to address dangerously low blood pressure promptly to prevent further complications and ensure your overall well-being. Remember, if you experience any of the signs mentioned above or suspect that your blood pressure is dangerously low, seek medical attention immediately.
Prevention And Treatment
A dangerous low blood pressure for a woman can cause severe symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, and weakness. It is important to seek immediate medical attention to prevent complications and receive appropriate treatment.
Maintaining A Healthy Blood Pressure
Prevention plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy blood pressure for women. By adopting certain lifestyle modifications, women can reduce the risk of low blood pressure and its potentially dangerous consequences. Here are some effective ways to keep your blood pressure within the normal range:
1. Stay Hydrated:
Keep your body hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Maintaining proper hydration levels helps to regulate blood pressure and prevent it from dropping to dangerous levels.
2. Eat a Balanced Diet:
Ensure your diet includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive salt and processed foods, as high sodium intake can lead to low blood pressure.
3. Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity to keep the heart and blood vessels healthy. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling.
4. Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive alcohol consumption can cause a drop in blood pressure. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation, which means up to one drink per day for women.
5. Avoid Prolonged Standing:
Standing for extended periods can cause blood to pool in the legs, leading to low blood pressure. Take breaks, sit down, or elevate your legs to improve blood circulation.
Medical Interventions
In severe cases, medical interventions may be necessary to prevent and treat dangerously low blood pressure. Healthcare professionals may recommend the following:
1. Medications:
In certain situations, medical professionals may prescribe medications to help regulate blood pressure. These medications might include fludrocortisone, midodrine, or alpha-beta blockers.
2. Intravenous Fluids:
In emergency situations, intravenous fluids might be administered to rapidly increase blood volume and stabilize blood pressure.
3. Compression Stockings:
For individuals with orthostatic hypotension, compression stockings can help improve blood flow and prevent drops in blood pressure when standing up.
4. Dietary Changes:
A healthcare professional may recommend increasing salt intake or adding more fluids to the diet to help raise blood pressure.
5. Regular Check-Ups:
Scheduling regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help monitor and manage blood pressure effectively. They can provide advice tailored to an individual's specific medical history and condition.
Credit: www.singlecare.com
Conclusion
To sum up, recognizing the dangers of low blood pressure in women is crucial for health and well-being. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and potential risks involved can aid in early identification and appropriate intervention. By prioritizing regular check-ups and seeking prompt medical attention when necessary, women can effectively manage low blood pressure and minimize its adverse effects on their health.






0 Comments