To stop sleep paralysis in the moment, focus on making small body movements like moving a finger. This helps to recover more quickly from sleep paralysis.
Sleep paralysis can be triggered while falling into or coming out of REM sleep, but it is not dangerous, and the things you see are not real. Sleeping on your side or stomach can help prevent sleep paralysis, as it is more common when sleeping on the back.
Furthermore, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and a good sleep environment can also aid in preventing future episodes of sleep paralysis. Avoiding sleep deprivation and maintaining an adequate sleeping schedule are key factors in preventing sleep paralysis.
Remember, staying calm and focusing on breathing can help release paralysis faster, and it's essential to be aware that sleep paralysis episodes will pass with time. Sleep paralysis can be a terrifying experience, leaving individuals feeling helpless and vulnerable.
Understandably, many seek ways to stop sleep paralysis in the moment to alleviate the distress it causes. This guide aims to provide valuable insights and practical tips for preventing and managing sleep paralysis episodes effectively.
Whether you have encountered sleep paralysis in the past or are looking for proactive methods to prevent it, the following information will empower you with helpful strategies and techniques.

Credit: www.oniri.io
Understanding Sleep Paralysis
During sleep paralysis, focus on making small body movements like moving your fingers to help recover more quickly. To prevent future episodes, stick to a set sleep schedule and avoid sleeping on your back.
Definition And Causes
Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that occurs during the transitional stages of sleep when a person is either falling asleep or waking up. It is characterized by the temporary inability to move or speak while being fully conscious.
During sleep paralysis, the brain's REM (Rapid Eye Movement) cycle is disrupted, leading to a state of immobility. The exact cause of sleep paralysis is not yet fully understood. However, researchers believe that it is often triggered by a disruption in the REM sleep cycle.
This disruption can be caused by various factors such as irregular sleep patterns, sleep deprivation, insomnia, stress, anxiety, and certain sleep disorders. Sleep paralysis can also be more likely to occur in individuals who have a family history of the condition.
Symptoms
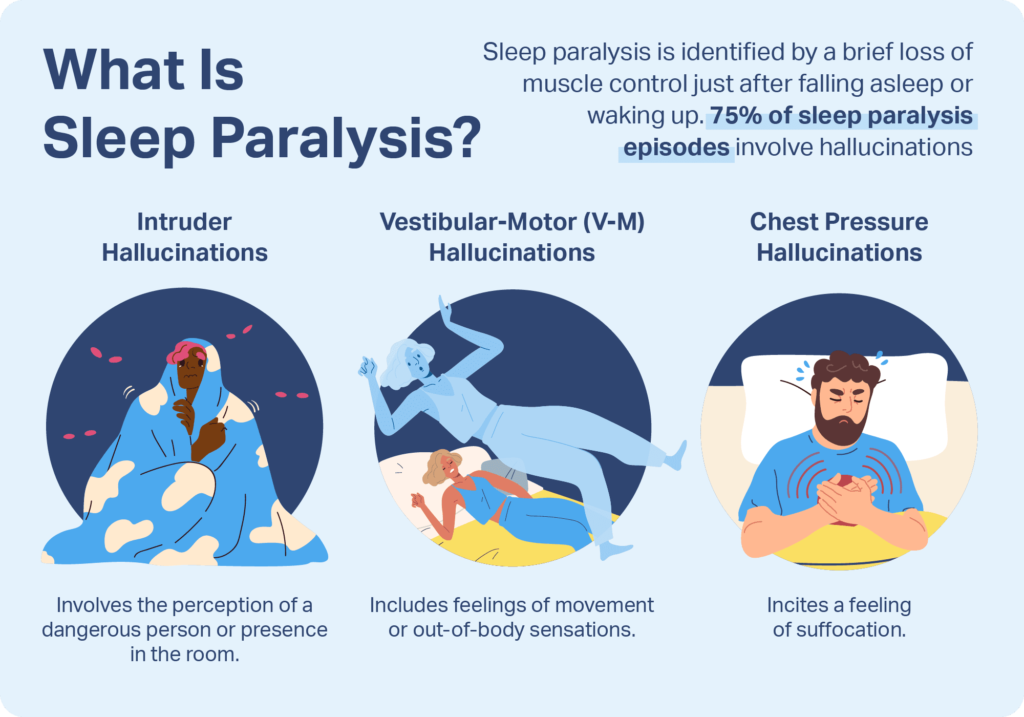
When experiencing sleep paralysis, individuals often report feeling a sense of pressure on their chest, as if something is sitting or pressing down on them. They may also perceive a presence in the room or have hallucinations, which can be vivid and terrifying.
These hallucinations can involve seeing or hearing things that are not actually present. Other common symptoms of sleep paralysis include a feeling of being paralyzed, difficulty breathing, and a heightened awareness of one's surroundings. The duration of sleep paralysis episodes varies, but they typically last for a few seconds to a few minutes.
Prevention
While it may not be possible to completely prevent sleep paralysis, there are some steps you can take to reduce the frequency of episodes. Here are a few tips:
1. Maintain a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at consistent times can help regulate your sleep cycle and decrease the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
2. Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make sure your bedroom is comfortable, quiet, and dark. Avoid distractions such as electronic devices before bedtime and consider using earplugs or eye masks if needed.
3. Practice stress management: Stress and anxiety can contribute to sleep disturbances, including sleep paralysis. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress levels and promote better sleep.
4. Improve sleep hygiene: Establish a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath. Avoid stimulants like caffeine or nicotine close to bedtime and create a comfortable sleep environment.
5. Sleep in a different position: Sleeping on your back can increase the likelihood of sleep paralysis episodes. Try sleeping on your side or stomach instead.
6. Seek treatment for underlying sleep disorders: If you have an underlying sleep disorder such as narcolepsy or sleep apnea, seeking treatment can help reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis.
Remember, while sleep paralysis can be a frightening experience, it is not dangerous and will pass on its own. By implementing these prevention strategies, you can potentially reduce the frequency of sleep paralysis episodes and sleep more peacefully.
Credit: www.sleepfoundation.org
How To Stop Sleep Paralysis In The Moment
If you experience sleep paralysis, you know how terrifying it can be to feel awake but unable to move. In the moment, it's crucial to know how to stop sleep paralysis and regain control over your body. Making small body movements, focusing on breathing, and adjusting your sleeping position are effective methods to overcome sleep paralysis as it occurs.
Making Small Body Movements
When experiencing sleep paralysis, remember that making small movements can help snap your body out of this frightening state. Try moving one finger at a time or wiggling your toes. These tiny motions can gradually awaken your body, relieving the paralysis faster.
Focusing On Breathing
Concentrating on your breathing can also aid in stopping sleep paralysis. Take slow, deep breaths and focus on each inhale and exhale. This mindfulness can calm your mind and body, facilitating a quicker recovery from sleep paralysis.
Sleeping Positions
Your sleeping position can influence the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. It is often triggered when sleeping on your back. To prevent future episodes, try sleeping on your side or stomach. Changing your sleeping position can reduce the frequency of sleep paralysis and make it easier to overcome when it does occur.
Preventing Future Episodes Of Sleep Paralysis
After experiencing a terrifying bout of sleep paralysis, it's natural to want to know how to prevent it from happening again. Here are some strategies for keeping sleep paralysis at bay:
Establishing A Sleep Schedule
One of the most effective ways to prevent future episodes of sleep paralysis is by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your internal body clock, reducing the likelihood of experiencing disruptive sleep patterns that can trigger sleep paralysis.
Creating An Ideal Sleep Environment
Your sleep environment plays a crucial role in preventing sleep paralysis. Ensure that your bedroom is conducive to quality sleep by keeping it dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows to create a cozy sleep sanctuary that promotes undisturbed rest.
Managing Underlying Conditions
Underlying medical or psychological conditions such as stress, anxiety, and sleep disorders can contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis. By effectively managing these conditions through therapy, medication, or relaxation techniques, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing future episodes of sleep paralysis.
Additional Tips For Better Sleep
Are you struggling with sleep paralysis? Here are some additional tips to help you stop sleep paralysis in the moment: focus on making small body movements, avoid sleeping on your back, sleep on your side or stomach, and stay calm by concentrating on your breathing.
These techniques can help you recover more quickly from sleep paralysis episodes.
Maintaining Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is not only important for overall health and fitness, but it can also contribute to better sleep. Engaging in physical activities during the day can help tire your body, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Exercise also releases endorphins, which can reduce stress and anxiety, common triggers for sleep paralysis. It is recommended to engage in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Remember to avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it may energize your body and make it difficult to fall asleep.
Relieving Stress
Stress is a major contributor to sleep problems, including sleep paralysis. Managing stress levels can help improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis episodes. There are various relaxation techniques and stress management strategies that you can incorporate into your daily routine.
Deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga are effective ways to relax your mind and body before bedtime. It's also important to establish a calming bedtime routine that includes activities such as reading a book or taking a warm bath. Avoid consuming stimulants such as caffeine or alcohol in the evening, as they can interfere with sleep and increase stress levels.
Improving Sleep Quality
Improving the overall quality of your sleep is crucial in preventing sleep paralysis. Creating a sleep-friendly environment can help signal your body that it is time to rest. Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows that support your body's natural alignment.
Establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your internal body clock and promotes better sleep. Avoid using electronic devices, such as smartphones or tablets, before bed as the blue light emitted can interfere with your sleep cycle. Instead, engage in relaxing activities that promote a sense of calmness.
Incorporating these additional tips into your daily routine can significantly improve your sleep quality and reduce the chances of experiencing sleep paralysis. Remember to be consistent and patient as it may take time for these changes to take effect. By prioritizing good sleep habits and taking steps to alleviate stress, you can promote restful sleep and wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated.

Credit: www.calm.com
Frequently Asked Questions On How To Stop Sleep Paralysis In The Moment
How Do You Stop Sleep Paralysis Fast?
To stop sleep paralysis fast, focus on making small body movements like moving your fingers. There are no proven therapies to stop an episode, but this technique helps people recover more quickly. Sleep on your side or stomach to prevent sleep paralysis, as it's more common when sleeping on your back.
Stay calm and concentrate on your breathing during an episode.
What Triggers Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is believed to be triggered by a disturbed rapid eye movement cycle during falling into or coming out of REM sleep.
Can I Force Myself Out Of Sleep Paralysis?
You cannot force yourself out of sleep paralysis. It will naturally pass with time. Focus on small body movements to help recover more quickly.
How Should I Sleep If I Have Sleep Paralysis?
To sleep better with sleep paralysis, try these tips: 1. Sleep on your side or stomach instead of your back. 2. Stay calm and focus on your breathing during an episode. 3. Try to make small body movements, like wiggling your fingers.
4. Maintain a regular sleep schedule and create a comfortable sleep environment. 5. Remember that sleep paralysis is not harmful and the things you see are not real. These practices can help prevent and manage sleep paralysis episodes.
How Do You Stop Sleep Paralysis Fast?
Most people find that focusing on small body movements, like moving a finger, can help them recover from sleep paralysis more quickly.
Conclusion
While there are no proven therapies to stop sleep paralysis in the moment, many individuals have found relief by focusing on small body movements. By making small movements, such as moving one finger at a time, individuals can help themselves recover from sleep paralysis more quickly.
It is important to remember that sleep paralysis is not dangerous and will pass with time. Sleeping on the side or stomach may also help prevent future episodes. Taking these steps can bring some relief to those experiencing sleep paralysis.






0 Comments