Tourniquet pain after knee replacement can last for approximately a month, but if the pain persists or worsens, it is advisable to contact your surgeon. During the early stages of recovery, it is normal to experience a tight band feeling caused by swelling, which should gradually subside within the first month.
However, if stiffness persists or worsens, it is important to seek medical advice. Recovery time can vary, with most people able to resume daily activities with reduced pain after three to six weeks, and full recovery taking anywhere from four months to a year.
The first few days after surgery may be the most painful, but pain medication will be provided to manage discomfort.
Duration Of Tourniquet Pain
The duration of tourniquet pain after knee replacement can vary, but it is typically temporary and should start to subside within the first month after surgery as swelling and stiffness decrease. However, if the pain persists or worsens, it is important to consult with your surgeon for further evaluation.
Typical Timeline For Tourniquet Pain After Knee Replacement
After undergoing knee replacement surgery, many patients experience tourniquet pain, which is the discomfort felt due to the use of a tourniquet during the procedure. While the duration of tourniquet pain can vary from person to person, there is a general timeline that can help patients understand what to expect during their recovery.
During the immediate post-surgery period, which typically lasts for the first few days, patients may experience the highest level of pain as their body adjusts to the surgical intervention. Pain medications prescribed by the doctor can help alleviate this discomfort and provide relief during this initial stage.
Within the first month after the surgery, tourniquet pain may still be present, albeit to a lesser extent. During this period, the knee may still be healing, and it is normal to experience some degree of discomfort. However, if the pain continues to worsen or becomes unbearable, it is important to consult with the surgeon for further evaluation.
As the recovery progresses, patients can typically expect a gradual reduction in tourniquet pain. Around three to six weeks after surgery, most individuals can resume their daily activities with reduced pain levels. However, it is crucial to note that full recovery can take anywhere from four months to a year, as the knee continues to heal and regain strength.
Factors That Can Affect The Duration Of Tourniquet Pain
While the typical timeline for tourniquet pain provides a general guideline, it is important to acknowledge that several factors can impact the duration of discomfort experienced by patients after knee replacement surgery. By understanding these factors, individuals can manage their expectations and work towards a smooth recovery.
One significant factor that can affect tourniquet pain duration is the individual's overall health and well-being. Patients who have pre-existing medical conditions or complications may experience prolonged discomfort compared to those who do not. Additionally, factors such as age, weight, and overall fitness level can also influence the healing process and, consequently, the duration of tourniquet pain.
The type and extent of the knee replacement surgery can also contribute to the duration of tourniquet pain. Complex procedures or revisions may result in prolonged discomfort. Moreover, the skill and technique of the surgeon can also play a role in minimizing tourniquet pain during the operation and subsequently affecting its duration during recovery.
Post-operative care and rehabilitation efforts can significantly impact the duration of tourniquet pain. Following the prescribed physical therapy exercises, adhering to pain management strategies, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can aid in a faster and smoother recovery process, potentially reducing tourniquet pain duration.
Managing And Alleviating Tourniquet Pain During Recovery
While tourniquet pain is expected during the recovery period after knee replacement surgery, there are several strategies that patients can employ to manage and alleviate the discomfort. It is important to note that these strategies should be discussed with a healthcare professional and tailored to individual needs.
One effective approach to managing tourniquet pain is the appropriate use of pain medications. Following the prescribed dosages and timings can help control pain levels and improve overall comfort. Additionally, the use of ice and heat therapy, as advised by healthcare professionals, can provide relief and reduce inflammation in the affected area.
Physical therapy and exercises are crucial for regaining strength and mobility after knee replacement surgery. Engaging in recommended exercises can not only expedite the recovery process but also help alleviate tourniquet pain. Working closely with a physical therapist and following their guidance can ensure that these exercises are performed correctly and safely.
Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or guided meditation, can also contribute to managing tourniquet pain. These techniques help relax the body and mind, ultimately reducing stress and tension that may exacerbate pain levels.
Ensuring proper nutrition and hydration is imperative for the body's healing process. A well-balanced diet with sufficient nutrients can support tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and promote overall wellness, potentially aiding in alleviating tourniquet pain.
Lastly, maintaining open communication with the healthcare team is vital throughout the recovery process. Reporting any persistent or worsening pain and discussing concerns allows for timely intervention and adjustments in the treatment plan, ensuring the best possible outcome.
Credit: www.atlantaboneandjoint.com
Potential Complications And Risks
Tourniquet pain typically lasts for the first few days after knee replacement surgery, but it should gradually subside within the first month of recovery. If the pain persists or worsens, it's important to contact your surgeon for further evaluation.
Possible Complications Associated With Tourniquet Use
Tourniquets are commonly used during knee replacement surgeries to minimize blood loss and provide a clearer surgical field. While they are generally considered safe and effective, there are potential complications associated with their use that patients should be aware of.
One possible complication is thigh pain following tourniquet application. Research has found that patients may experience discomfort in the thigh area as a result of the pressure applied by the tourniquet. This pain typically lasts for about one month after surgery and gradually subsides as the knee heals.
In addition to thigh pain, the use of tourniquets during knee replacement surgeries may also increase the risk of complications. A study published by the National Institutes of Health found that tourniquet use can have negative effects on quadriceps function and pain levels up to 12 months post-surgery.
To minimize the risk of complications, surgeons carefully consider the duration and pressure applied by the tourniquet. However, it is important for patients to be aware of these potential risks and discuss them with their surgeon prior to the procedure.
Long-term Effects Of Tourniquet Use On Knee Replacement Outcomes
While tourniquets can be effective during knee replacement surgeries, there is ongoing debate regarding their long-term effects on patient outcomes. Some studies suggest that tourniquet use may have positive effects on surgical outcomes, such as reduced blood loss and improved visualization for the surgeon.
On the other hand, other research suggests that tourniquets may have negative long-term effects on knee replacement outcomes. The prolonged pressure applied by the tourniquet can cause tissue damage and muscle weakness, which may affect the overall functioning of the knee joint.
The decision to use a tourniquet during knee replacement surgery involves a balance between the potential benefits and risks. Surgeons will carefully assess each patient's individual situation, taking into consideration factors such as age, pre-existing conditions, and the complexity of the surgery.
It is important for patients to have an open discussion with their surgeon about tourniquet use and its potential long-term effects. By understanding the risks and benefits, patients can make informed decisions about their knee replacement procedure.
Treatment And Pain Management
After knee replacement surgery, tourniquet pain may last for several weeks to a few months. It is a normal part of the recovery process, but if the pain persists or worsens, it is important to consult with your surgeon.
Medical Interventions For Tourniquet Pain Relief
After knee replacement surgery, tourniquet pain can be a common side effect. Luckily, medical interventions can help alleviate this discomfort. Here are some common medical treatments for tourniquet pain relief:
- Pain medication: Your doctor may prescribe pain medications, such as opioids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), to manage tourniquet pain. These medications help reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
- Nerve blocks: Nerve blocks are another effective method used to manage tourniquet pain. Local anesthesia is injected near the nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals, providing temporary pain relief.
- Corticosteroid injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and relieve tourniquet pain. These injections can provide longer-term pain relief and improve overall mobility.
Non-pharmacological Approaches To Manage Tourniquet Pain
In addition to medical interventions, non-pharmacological approaches can also play a crucial role in managing tourniquet pain after knee replacement surgery. These methods focus on promoting overall well-being and include:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy is often recommended to improve strength and flexibility, reduce pain, and enhance overall function. A qualified physical therapist can guide you through exercises and techniques specifically designed for tourniquet pain management.
- Heat and cold therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce swelling and alleviate tourniquet pain. Heat therapy promotes blood flow and relaxation, while cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb the area.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS): TENS therapy involves using a small device that transmits low-voltage electrical currents to targeted areas on the skin. This can disrupt the pain signals and provide temporary relief from tourniquet pain.
Physical Therapy And Rehabilitation Techniques For Pain Reduction
Physical therapy and rehabilitation play a vital role in alleviating tourniquet pain and promoting long-term recovery after knee replacement surgery. Here are some techniques commonly used:
- Range of motion exercises: These exercises help improve joint flexibility, reducing stiffness and tourniquet pain. A physical therapist can guide you through gentle movements to ensure safe and effective recovery.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee can provide stability and support, reducing pain and enhancing overall function. Your physical therapist will recommend exercises targeting specific muscle groups.
- Balance and proprioception exercises: Improving balance and proprioception (awareness of body position) can help prevent falls and reduce the risk of additional knee injuries. Your physical therapist will guide you through exercises that challenge and improve these skills.
- Manual therapy techniques: Physical therapists may use manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilization or soft tissue mobilization to reduce tourniquet pain, improve range of motion, and enhance overall function.
Prevention And Future Directions
Tourniquet pain after knee replacement surgery is a common concern. While some discomfort is expected during the early stages of recovery, it should begin to subside within the first month. If the pain persists or worsens, it is important to consult your surgeon.
Emerging Strategies To Minimize Tourniquet Pain
As medical research continues to advance, healthcare professionals are constantly exploring new strategies to minimize tourniquet pain after knee replacement surgery. These emerging strategies aim to enhance patient comfort and promote a smoother recovery process. Here are some cutting-edge approaches that show promising results:
1. Pharmacological interventions: Researchers are investigating the use of novel medications and local anesthetics to alleviate tourniquet pain. This includes the administration of analgesics before surgery and the incorporation of long-acting anesthetics into the surgical site. These interventions aim to reduce both acute and chronic postoperative pain, allowing patients to experience a more manageable recovery period.
2. Targeted nerve blocks: Nerve blocks have long been used to provide postoperative pain relief. However, advancements in imaging techniques and the development of more precise delivery systems have paved the way for targeted nerve blocks. By precisely targeting the nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals, healthcare providers can provide highly effective pain relief while minimizing potential side effects.
3. Cryotherapy and cold compression therapy: Cold therapy has been known for its analgesic properties and ability to reduce inflammation. Recent studies have shown the positive effects of cryotherapy and cold compression therapy in managing tourniquet pain after knee replacement surgery. These techniques involve the application of cold temperatures to the affected area, helping to decrease pain and swelling, and promoting a faster recovery.
Advancements In Tourniquet Technology And Techniques
Advancements in tourniquet technology and techniques have also played a significant role in minimizing tourniquet pain after knee replacement surgery. Healthcare professionals now have access to more sophisticated tools and methods that promote patient comfort and safety. Here are a few notable advancements:
1. Pneumatic tourniquet systems: Traditional tourniquet systems used to be manual and prone to inconsistent pressures. However, pneumatic tourniquet systems have revolutionized the field. These systems allow precise control of tourniquet pressure, ensuring optimal blood flow restriction and minimizing postoperative pain and complications.
2. Personalized tourniquet pressure: Recent studies have highlighted the importance of individualizing tourniquet pressure based on patient-specific factors such as limb circumference and blood pressure. By tailoring the tourniquet pressure to each patient's needs, healthcare professionals can reduce unnecessary pain and optimize surgical outcomes.
3. Tourniquet monitoring devices: Monitoring devices have been developed to provide real-time feedback on the tourniquet pressure, duration, and any potential issues. These devices help healthcare providers ensure appropriate pressure levels, minimize the risk of complications, and ultimately reduce postoperative pain.
Research And Clinical Trials Aimed At Reducing Tourniquet-related Discomfort
Research and clinical trials are essential in identifying innovative techniques and interventions to reduce tourniquet-related discomfort after knee replacement surgery. Scientists and healthcare professionals are actively investigating various approaches to improve patient outcomes. Here are some noteworthy areas of research:
1. Tourniquet pressure optimization: Researchers are working to determine the optimal tourniquet pressure that provides adequate blood flow restriction while minimizing pain and tissue damage. By fine-tuning this parameter, healthcare providers can improve patient comfort during and after surgery.
2. Tourniquet release protocols: Studies are exploring the optimal timing and technique for releasing the tourniquet after surgery. Early tourniquet release protocols aim to minimize the duration of blood flow restriction, potentially reducing postoperative pain and complications.
3. Patient-reported outcomes: Researchers are increasingly emphasizing the importance of patient-reported outcomes, such as pain scores and functional assessments. By incorporating patient perspectives, researchers can identify factors that contribute to tourniquet-related discomfort and develop targeted interventions to address these issues.
4. Novel tourniquet designs: Innovative tourniquet designs are being explored to improve patient comfort and safety. These designs focus on minimizing pressure points, optimizing pressure distribution, and enhancing ease of use for healthcare providers.
In conclusion, ongoing research and technological advancements in tourniquet technology, along with the development of innovative strategies, are working towards minimizing tourniquet pain after knee replacement surgery. These developments are aimed at improving patient satisfaction, promoting a faster recovery, and enhancing overall surgical outcomes.
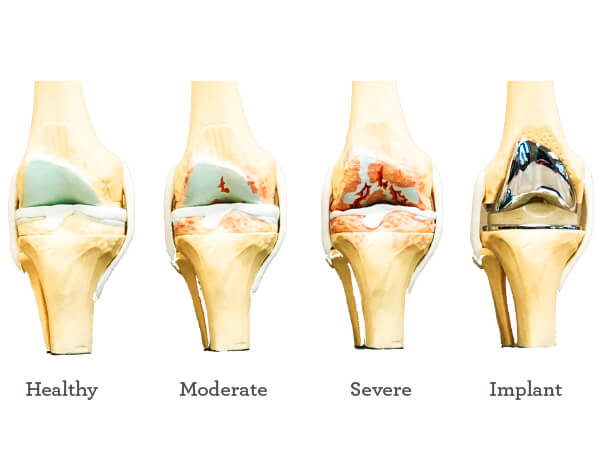
Credit: orthonebraska.com
Frequently Asked Questions On How Long Does Tourniquet Pain Last After Knee Replacement
How Do You Treat Tourniquet Pain?
Treat tourniquet pain by giving it time to gradually subside within the first month after the procedure. Contact your surgeon if the pain persists or worsens. Full recovery can take up to a year. Pain medication can be used to manage pain during the early stages of recovery.
How Long Does Tight Band Feeling Last After Knee Replacement?
The tight band feeling after knee replacement usually lasts for the first month or so. It is a normal part of the recovery process due to swelling and stiffness. If the stiffness persists or worsens, contact your surgeon. Full recovery can take anywhere from four months to a year.
How Long Does It Take For A Total Knee Replacement To Stop Hurting?
Most people can resume daily activities with reduced pain about three to six weeks after total knee replacement surgery. Full recovery may take four months to a year. Your body needs time to heal after major surgery.
Conclusion
Tourniquet pain after knee replacement surgery is a common concern during the recovery process. While it is normal to experience some discomfort and tightness in the early stages, this should improve within the first month or so. However, if the pain persists or worsens, it is important to consult with your surgeon.
Remember, every individual's experience may vary, so be patient with your body as it heals.






0 Comments